Google's quantum chip Willow has been released. Under the threat of super computing power, will the 1 million bitcoins held by Satoshi Nakamoto be frozen to ensure their safety?
Author: Weilin, PANews
On December 10, Google introduced its latest quantum chip Willow in its official blog, which triggered another heated discussion in the crypto community about quantum computing attacks. Will quantum computing undermine existing encryption security mechanisms, especially pose a threat to mainstream cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin?
Partly affected by the news, as of 14:20 pm on December 10, according to Coinglass data, a sharp crypto market pullback triggered $1.758 billion in liquidations within 24 hours.
Google launches new quantum chip "Willow"
Google announced in a blog post that the "Willow" quantum chip has achieved two major achievements. First, as the number of quantum bits (qubits, the unit of measurement for quantum information) increases, Willow is able to achieve an exponential reduction in error rates, overcoming the key challenges that the field of quantum error correction has been trying to solve for nearly 30 years. Second, Willow completed a standard benchmark calculation in less than five minutes, while the same computing task would take even today's fastest supercomputer 10^25 years to complete, a number far exceeding the age of the universe.
"This provides credible support for the idea that quantum computing takes place in multiple parallel universes, which fits with the theory that we live in a multiverse, a prediction first proposed by David Deutsch," Hartmut Neven, founder and head of Google Quantum AI, said in a blog post.
Quantum bits (qubits) are the basic unit of information and the core of quantum computing; the more qubits there are, the stronger the computing power. However, increasing the number of qubits also brings a higher risk of error. If the error rate is too high, the calculation will become unreliable and produce wrong results, which will make it difficult for quantum technology to achieve practical large-scale applications.
On December 9, Google CEO Sundar Pichai said in an X post that Willow is an important step for Google on the road to building a "practical quantum computer" and that the technology has practical application potential in areas such as drug development, nuclear fusion energy, and battery design.
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk expressed his admiration for Google's invention in response to Pichai's tweet. Pichai replied that they would cooperate on Starship's quantum cluster in the future.
Cryptocurrency security faces challenges? Opinions vary
Does Willow pose a threat to cryptocurrencies? Advances in quantum computing have long been seen as a potential turning point for the crypto industry. If quantum computers can crack current encryption algorithms, it could quickly expose user funds and pose a huge risk of theft. However, opinions vary on this.
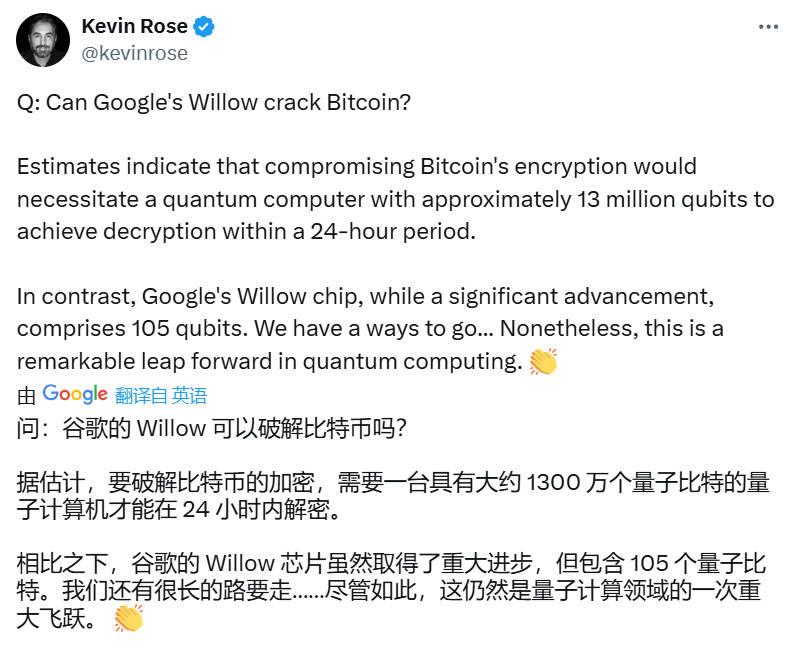
Kevin Rose, a tech entrepreneur and former senior product manager at Google, said in a Dec. 9 X post that Willow is far from a threat to cryptocurrencies at this point. Rose noted that estimates of cracking Bitcoin encryption would require a quantum computer with about 13 million qubits to decrypt it in 24 hours. "In comparison, Google's Willow chip, while an important advance, has only 105 qubits," he said.
Avalanche founder Emin Gün Sirer said this morning that the latest developments in quantum computing are indeed amazing, but at least they do not pose a threat to the security of cryptocurrencies for now. Current quantum computing is only suitable for performing a few types of tasks such as digital factorization, and cannot do tasks such as reversing one-way hash functions. The designs of mainstream blockchains including Bitcoin and Avalanche are all quantum-resistant, with a short exposure time for public keys and a short computing window for attackers. Therefore, quantum computing will not threaten cryptocurrencies in the short term. In the future, when the quantum threat really comes, blockchains such as Avalanche can also quickly add quantum-resistant signatures.
Dragonfly partner Haseeb Qureshi holds a similar view, citing a Metaculus research report, saying that the Shor algorithm is expected to take until around 2040 to crack the RSA key for the first time.
Another Bitcoin OG, Ben Sigman, also noted in his X-Platform post that Bitcoin users should not worry about the invention, stating that “crypto technology remains secure… at least for now.”
Still, David Marcus, CEO of payments platform Lightspark, said he believes most people "have not yet fully understood" the significance of Google's breakthrough. Marcus noted that it means "post-quantum cryptography and encryption technology need to accelerate development."
In fact, Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin has proposed a way to mitigate the risks of quantum computing, explaining in a March X post that this problem can be solved through a simple hard fork. Buterin said that the blockchain would need to undergo a hard fork, and users would need to download new wallet software, and most users would not lose their funds.
Quantum computing and Bitcoin, experts suggest freezing Satoshi Nakamoto's 1 million BTC
The proof-of-work (POW) mechanism that is crucial to Bitcoin's operation requires miners to solve complex mathematical problems to verify transactions and ensure the security of the network. However, quantum computing, with its unprecedented computing speed, could threaten this balance.
Quantum algorithms like Grover’s algorithm are theoretically capable of solving these problems faster than conventional computers. As such, the technology has the potential to centralize mining power, undermining Bitcoin’s decentralized philosophy.
According to estimates by Dan A. Bard, a faculty member at the University of Kent, if the hash rate of the Bitcoin network continues to grow at the same rate as Moore's Law compared to the current value of quantum computing technology, it will take about 27 years until a single quantum computer can completely surpass other miners in the network and completely control the network.
In addition, Bitcoin's elliptic curve cryptography (ECC), a key technology for protecting wallet addresses, is also at risk. Quantum computers may use the Shor algorithm to crack ECC in the future, exposing Bitcoin transactions to potential security vulnerabilities. This vulnerability particularly affects well-known early addresses, including a considerable portion of Bitcoin held by Bitcoin founder Satoshi Nakamoto.
Emin Gün Sirer mentioned above mentioned this more serious situation in his reply to Haseeb's post: "Haseeb reminded me that Satoshi's 1 million bitcoins may indeed have quantum threat issues. Early Bitcoin used a very old Pay-To-Public-Key format, which leaks public keys and gives attackers time to study, which is the source of all crypto bounties. Modern Bitcoin wallets or modern systems such as Avalanche do not use P2P K, but it did exist in the early stages of Bitcoin. Therefore, as the quantum threat intensifies, the Bitcoin community may need to consider freezing Satoshi's 1 million bitcoins, or more generally, providing a final date and freezing all bitcoins on P2P K UTXOs."
“Once the public key is known, Shor’s algorithm, adapted for ECDSA, can be run on an ideal quantum computer to find the public key in polynomial time. Traditional methods of finding the solution are superpolynomial and several orders of magnitude slower… Polynomial time is potentially feasible, and researchers speculate that eventually ECDSA will be cracked by quantum computers,” wrote researchers at Acheron Trading.
Meanwhile, the Bitcoin community seems unlikely to move away from the Proof of Work (POW) mechanism to alternative consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake (POS). Even cryptographer Adam Back said that PoS cryptocurrencies lack immutability, decentralization, and verifiable high production costs, highlighting their fundamental differences from Bitcoin.
“As hard currency, it is immutable, decentralized, and has a verifiable cost to produce. The technical structure is designed to make it economically stable and practically difficult to modify. PoS coins do not have these characteristics, they have CEOs and dozens of competitors. Bitcoin only has one,” Back said.
This resistance to change reflects the Bitcoin community’s concern about and importance of responding to the quantum threat. Although the threat of quantum computing has not yet been fully realized, active prevention measures are still key to protecting the Bitcoin network from future quantum attacks.
But others, including some quantum computer developers, say such concerns are unnecessary, saying that by the time quantum computers become reliable and powerful enough to attack Bitcoin, blockchain developers will have already patched the vulnerabilities that allow them to be hacked.
You May Also Like

The Role of Blockchain in Building Safer Web3 Gaming Ecosystems
- Immutable Ownership of Assets Blockchain records can be manipulated by anyone. If a player owns a sword, skin, or plot of land as an NFT, it is verifiably in their ownership, and it cannot be altered or deleted by the developer or even hacked. This has created a proven track record of ownership, providing control back to the players, unlike any centralised gaming platform where assets can be revoked.
- Decentralized Infrastructure Blockchain networks also have a distributed architecture where game data is stored in a worldwide network of nodes, making them much less susceptible to centralised points of failure and attacks. This decentralised approach makes it exponentially more difficult to hijack systems or even shut off the game’s economy.
- Secure Transactions with Cryptography Whether a player buys an NFT or trades their in-game tokens for other items or tokens, the transactions are enforced by cryptographic algorithms, ensuring secure, verifiable, and irreversible transactions and eliminating the risks of double-spending or fraudulent trades.
- Smart Contract Automation Smart contracts automate the enforcement of game rules and players’ economic exchanges for the developer, eliminating the need for intermediaries or middlemen, and trust for the developer. For example, if a player completes a quest that promises a reward, the smart contract will execute and distribute what was promised.
- Anti-Cheating and Fair Gameplay The naturally transparent nature of blockchain makes it extremely simple for anyone to examine a specific instance of gameplay and verify the economic outcomes from that play. Furthermore, multi-player games that enforce smart contracts on things like loot sharing or win sharing can automate and measure trustlessness and avoid cheating, manipulations, and fraud by developers.
- Cross-Platform Security Many Web3 games feature asset interoperability across platforms. This interoperability is made viable by blockchain, which guarantees ownership is maintained whenever assets transition from one game or marketplace to another, thereby offering protection to players who rely on transfers for security against fraud. Key Security Dangers in Web3 Gaming Although blockchain provides sound first principles of security, the Web3 gaming ecosystem is susceptible to threats. Some of the most serious threats include:

Vitalik Buterin Challenges Ethereum’s Layer 2 Paradigm
